GeneSafe Complete test
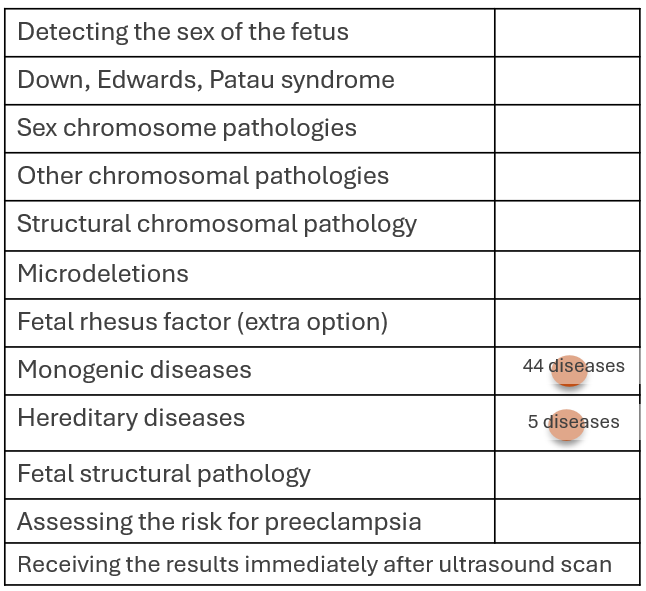
The aim of the GeneSafe Complete test is to find out about 29 different fetal single gene pathologies that can cause 44 different de novo and 5 hereditary genetic diseases that are not very often detectable on ultrasound and often only appear in late pregnancy or the first years of life. The incidence of monogenic disorders does not depend on the woman’s age, however, such diseases are more common when the biological father of the fetus is older.
The incidence of monogenic disorders does not depend on the woman’s age, however, such diseases are more common when the biological father of the fetus is older. We recommend performing the GeneSafe Complete test if the child's father is over 40 years old.
- The GeneSafe Complete requires a mother's venous blood test and a father's oral mucosa DNA test using a swab.
- The GeneSafe Complete test is carried out whose pregnancy has lasted at least 10 full weeks (10 weeks + 0 days). If you want to know the duration of your pregnancy, please visit our pregnancy calendar.
- It is not possible to find out the sex of the fetus with the test.
- The patient receives a response 21 business day after the blood test has been performed.
The test price includes a very early ultrasound examination of fetal developmental defects. Additionally, it covers a pre-test consultation that offers a detailed overview of the test's purpose, reliability, error rate, and alternative methods of testing.
Very early fetal developmental ultrasound with the NIPT tests is the most accurate combined prenatal screening method for the early detection of children with chromosomal diseases. The purpose of an ultrasound scan is to first determine the size of the pregnancy, to assess the presence and type of a possible multiple pregnancy, and then to exclude situations in which the NIPT test should not be performed. Since the NIPT test cannot detect structural developmental defects in a child, the objective of the ultrasound examination of very early developmental defects in the fetus is to exclude 10 severe developmental defects in the child.