A fetal anatomic scan at 20- 21 weeks of pregnancy helps to detect abnormalities in the development of the fetus and the risks of premature birth.
The ultrasound examination of fetal developmental defects is one of the most important ultrasound examinations during pregnancy. This examination is performed using abdominal transducers on weeks 19 to 21+6 of the pregnancy. In this size of pregnancy, the fetus has developed all organs and begins its period of growth and maturation. At the 20th week of pregnancy, about half of the pregnancy has passed and the other half awaits. The fetus weighs 300–350 g at this time, and its weight will increase nearly tenfold over the next few months. The fetus already resembles a child, but does not know how to smile yet, because the mimic muscles of their face have not yet developed. The fetus already opens its mouth and swallows and breathes amniotic fluid, sensing its smell and taste. Their inner ear has already developed, so they hear the sounds coming from the womb: the mother's heartbeat, the breathing sounds of the lungs, the movement of the bowel. At the same time, they are not yet able to distinguish sounds coming from outside the womb, such as their father's speech. The fetal skin is covered with small hairs and vernix caseosa to protect the fetus from the soaking effects of amniotic fluid. They already have eyebrows and formed eyelids, but their eyes are covered with embryonic film, so they can't open them yet. The fetus still lacks hair and eyelashes, but nails are beginning to form on the tips of fingers and toes. The size of the fetal heart corresponds to the size of the €1 coin and the heart beats 120–160 times per minute. This is twice as fast as the mother's, that is, the mother's and father's heartbeats combined.
The ultrasound examination evaluates the placental placement, structure and umbilical cord attachment to the placenta. It is important to assess that the lower edge of the placenta and the blood vessels in the placenta do not cover the cervix and do not impede the birth of the child in the future. The amount of amniotic fluid is estimated so there is not too little or too much. By measuring the size of the fetal skull, the abdominal circumference and the length of the femur, it is possible to estimate the size of the child and specify their date of birth. It is very important to evaluate the organ structures of the fetus in detail. Attention is paid to the integrity of the brain skull and to the opening of the sutures and fissures of the skull bone so that the fetal brain tissue can grow unhindered. Brain structures and their correlation with the size of the pregnancy are assessed. Attention is paid to the child's eyes and their distance. The fullness of the upper lip is also assessed, so that they would have a nice smile in the future. The lower jaw of the fetus is evaluated so that it can cope with sucking in the future. Attention is paid to the integrity of the fetal spine and the anterior abdominal wall, as well as to the umbilical cord rising from the abdomen.
Attention is paid to the presence or absence of ultrasound features characteristic of fetal chromosomal diseases and the need for an amniocentesis is assessed accordingly.
The integrity, position and movement of the fetal arms and legs is assessed. The fetus bends and stretches its arms and legs and can already close and open its palm. Attention is paid to the presence and structure of the kidneys and their function is assessed as well. The assessment also includes checking whether the bladder is full and whether the bladder is surrounded by two umbilical cord arteries. Attention is paid to the fact that the fetal esophagus would be penetrable, and the stomach is filled and located on the same side with the heart - on the left. Special attention is paid to the heart structures of the fetus: the heart having four chambers, large blood vessels coming from the right chambers, and a regular heartbeat.
During this particular ultrasound examination, it is also possible to assess the gender of the child at the request of the family. Furthermore, if the child is in a suitable position, it is possible to get a color image of their face or a video recording of the ultrasound examination along with the doctor's explanations.
At the end of the ultrasound examination, the results of the ultrasound examination are explained to the family. In the presence of deviations, the nature, cause and prognosis of the deviation concerning the fetus are explained precisely.
The results of the ultrasound examination are sent through the Tricefy cloud service to the woman's mobile phone and e-mail address and, with the woman's consent, uploaded to the e-Health patient portal, where the results of the ultrasound examination will also be visible to the midwife or gynecologist monitoring the woman's pregnancy.
-
What you need to know before coming for a fetal ultrasound examination:
- the bladder must be emptied prior to the ultrasound examination;
- you must drink at least 2 liters of liquid per day on the previous two days;
- It is recommended to eat something 30 minutes before the examination;
- the abdominal skin should not be creamed and a belly button piercing has to be removed before the examination.
One of the most important complications of pregnancy is giving birth before the 34th week of pregnancy. However, premature birth is often accompanied by problems later in life, such as learning difficulties and neurological problems. Preeclampsia and cervical insufficiency are the most common causes of premature birth.
As an additional service, in the framework of ultrasound examination of fetal developmental defects, it is also possible to perform the following procedures:
-
Preeclampsia screening
During the second trimester ultrasound examination of fetal developmental defects, it is possible to identify 95% of women who develop preeclampsia before the 32nd week of pregnancy, and 90% of women who develop preeclampsia between weeks 32 and 36 of their pregnancy.
Based on the results of the OSCAR test in women at high risk, it is possible to reassess the risk of preeclampsia in order to determine the effect of prophylactic aspirin treatment. Preeclampsia risk assessment is also suitable for women who had not previously been assessed for preeclampsia risk or who were in the low-risk group as a result of the OSCAR test, because the assessment is the more accurate the closer the moment of developing preeclampsia is.
In order to perform the preeclampsia screening, the woman needs to come to the midwife's appointment on the day before the ultrasound examination, where blood pressure, weight and height are measured, and venous blood is taken for placental hormones. On the following day, in addition to screening for fetal developmental defects, the doctor also performs an assessment of the blood flow in the woman's uterine arteries. At the end of the ultrasound examination, a special risk calculation program calculates a woman's individual risk of preeclampsia. If the risk turned out to be high, the doctor will advise the woman on how to prepare an individual pregnancy plan.
-
Screening for spontaneous preterm birth
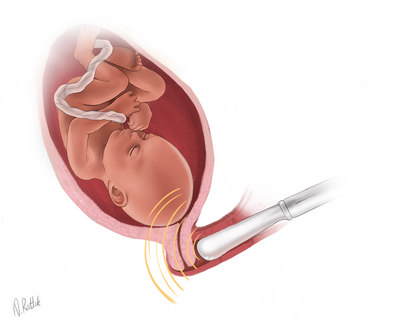
More than 50% of spontaneously occurring premature births are caused by cervical insufficiency, which is anatomically often expressed as a short cervix. In the case of cervical insufficiency, the cervix opens, the amniotic fluid breaks out and a premature birth has started.
For the screening of cervical insufficiency, it is necessary to come to the ultrasound examination with an empty bladder. At the end of the ultrasound examination, the doctor, with the consent of the woman, measures the length of the cervix using a vaginal transducer. Combining the length of the cervix with the history of obstetrics in a woman, a special risk calculation program calculates the individual risk of preterm birth for the woman.
With an increased risk of premature birth, there is an option of vaginal progesterone treatment up to 34 weeks of pregnancy. Vaginal progesterone treatment reduces the number of births before the 34th week of pregnancy by 45%. If, despite vaginal hormonal therapy, the cervix does shorten over the next few weeks, the doctor will refer the woman to a hospital for a cervical support suture.