SMART test
The SMART test is an innovative and modern first trimester combined screening. It combines the strengths of two different non-invasive fetal extracellular DNA tests with the advantages of two high-tech ultrasound examinations of the fetus at different stages of development.
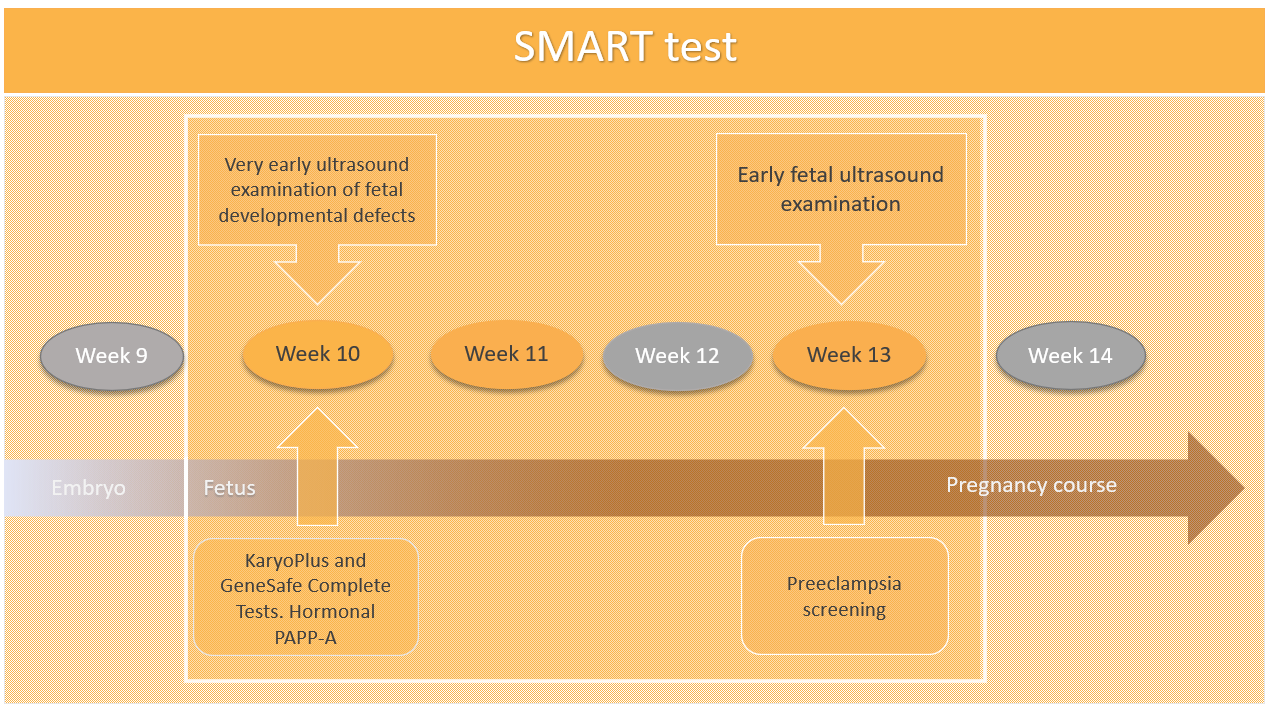
SMART test, a very early ultrasound examination of fetal developmental defects together with KaryoPlus and GeneSafe Complete test at the 10th week of pregnancy and the combination of these studies with early detailed ultrasound diagnosis of the fetus and assessment of maternal risks during gestation at the 13th week of pregnancy, is currently one of the most accurate combined prenatal screening tests for the early detection of chromosomal and gene diseases and congenital developmental defects in children.
-
The SMART test consists of the following separate studies:
- The purpose of very early ultrasound examination of fetal developmental defects is, firstly, to specify the size of the pregnancy and to assess the presence of a twin pregnancy and its type, and, secondly, to exclude situations where a NIPT test should not be performed. Since it is impossible to detect structural developmental defects in a child with the NIPT test, the purpose of a very early ultrasound examination of developmental defects in the fetus is to exclude 10 severe congenital developmental defects in the child.
- The PrenatalSafe Karyo Plus test enables the detection of other chromosomal numerical and structural pathologies and 9 clinically significant microdeletions in the mother's venous blood, in addition to Down, Edwards, and Patau syndrome, as well as the sex chromosome pathologies, all of which significantly affect the child's health.
- With the GeneSafe Complete test, it is possible to obtain information about the pathology of 29 different fetal single genes, which can cause 44 different de novo and 5 hereditary genetic diseases that are not very often detected by ultrasound examination and often manifest themselves only in the late period of pregnancy or in the first years of life.
- Early detailed fetal ultrasound with early echocardiography at the 13th week of pregnancy provides an opportunity to detect up to 100 different congenital developmental defects in the fetus. The ultrasound examination also measures the blood flow indices in the woman's uterine arteries and the length of the cervix, on the basis of which it is possible to assess the possibility of preeclampsia, intrauterine growth retardation and premature birth during a given pregnancy.
- The purpose of very early ultrasound examination of fetal developmental defects is, firstly, to specify the size of the pregnancy and to assess the presence of a twin pregnancy and its type, and, secondly, to exclude situations where a NIPT test should not be performed. Since it is impossible to detect structural developmental defects in a child with the NIPT test, the purpose of a very early ultrasound examination of developmental defects in the fetus is to exclude 10 severe congenital developmental defects in the child.
This combined screening helps to early detect nearly 100 different severe chromosomal or gene diseases and congenital developmental defects in the fetus that would otherwise remain undetected before birth or would only be detected later in pregnancy.
-
The SMART test can detect the diseases listed below:
- Aneuploidy of chromosome 22 (including Down syndrome)
- Sex chromosome anomalies (including Turner syndrome)
- Rare chromosome deletions and duplications <7Mb (including Williams syndrome)
- 9 clinically significant microdeletions (including DiGeorge syndrome)
- 44 different genetic diseases (including Noonan syndrome)
- 5 hereditary monogenic diseases (including cystic fibrosis)
- Major severe congenital developmental defects (including spina bifida)
- Major severe heart defects (including transposition of large arteries)
In addition to detecting the pathology of the fetus, the SMART test also provides an opportunity to find those women who may develop the following serious complications during pregnancy:
- Preeclampsia, in which the woman's kidney and liver function is disrupted, protein enters the urine and develops high blood pressure, which in more severe cases may be accompanied by a life-threatening seizure syndrome.
- Intrauterine growth retardation of the fetus, where the child does not reach its potential growth and lags in growth behind its peers. Due to a lack of food and oxygen, the gynecologist must monitor the growth and well-being of these fetuses with ultrasound more often and, if necessary, induce childbirth prematurely if the child's condition worsens.
- Premature birth due to a change in the structure of the cervix, as a result of which the cervix opens unnoticed during pregnancy, and the baby is born prematurely, when it is not yet able to cope with breathing outside the womb, maintaining the temperature and sucking on its own.
The SMART test is the best choice for parents who want to get as much information as possible about pregnancy risks and their yet-unborn child
The SMART test consists of two steps:
- Step ONE: Pre-NIPT ultrasound scan and blood test for PrenatalSafe Complete Plus test (PrenatalSafe Karyo Plus test + GeneSafe Complete test) along with blood test to determine placental hormones with pregnancy history and measurement of arterial blood pressure, weight and height at the 10th week of pregnancy. In addition to the mother's venous blood analysis, the test also requires an analysis of the child's father's oral mucosa.
- Step TWO: Early diagnostic ultrasound examination of developmental defects in the fetus at the 13th week of pregnancy and immediately after this explanation of the results of the SMART test, answering questions and, if necessary, giving recommendations for a pregnancy management plan.
It is important to emphasize that if the GeneSafe test requires additional in-depth analysis from the laboratory, the turnaround time for receiving the test results may be extended beyond the previously promised 7-10 days. In this case, the result of the GeneSafe test will not be available by the day of the ultrasound examination but will be sent encrypted to the patient's email as soon as the test result arrives at the laboratory, along with explanations from the doctor.
In conclusion
- Combined screening is carried out for those whose pregnancy has lasted at least 10 full weeks (10 weeks + 0 days). If you would like to know the duration of your pregnancy, please visit our pregnancy calculator.
- With the combined test, you can also find out the gender of the fetus if desired. We offer the SMART test only for singleton pregnancies.
- If the blood test is given at the 10th week of pregnancy, then the written response of the combined screening will be known to the woman immediately after the ultrasound examination at the 13th week of pregnancy.
It is essential to highlight the following points:
- The SMART test is not a substitute for the diagnostic ultrasound examination for fetal malformations conducted at the 20-week mark of pregnancy. The first-trimester ultrasound cannot identify all potential malformations.
- As a non-invasive screening test, the SMART test cannot detect all chromosomal and genetic disorders that can be identified through diagnostic amniocentesis performed at the 16-week stage of pregnancy.